1. The Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a methodological framework supporting the risk management process within IFSCA. It provides guidance for identifying, assessing, managing, reporting, and monitoring risks within the articulated risk tolerance limits of the IFSCA and offers reasonable assurance regarding the achievement of IFSCA’s objectives.
It aims to raise awareness among each employee of IFSCA of their active role in managing the risks linked to the activities under their responsibility. By implementing a systematic, consistent, and structured risk management approach across the enterprise, IFSCA should be able to identify, monitor, and control the risks it is exposed to in the conduct of its functions. Integrating enterprise risk management practices throughout the organisation helps achieve sustainable growth and enhance performance.
2. Risk Culture
2.1 Risk culture is the shared values, attitudes, competencies, and behaviors throughout the IFSCA that shape and influence governance practices and risk decisions. Risk culture pertains to the Authority’s risk approach and is critical to sound risk management governance. An effective risk culture is one that enables and rewards individuals and groups for taking the right risks in an informed manner.
2.2 To promote a sound risk culture, the top management establishes the tone by promoting risk awareness within a sound risk culture. These expectations shall be conveyed to all staff, who will be responsible for ensuring the Authority operates within the established risk appetite and limits.
3. As per the Committee of Sponsoring Organisations (COSO) Integrated Framework, ERM consists of the following eight interrelated components that are derived from the way management runs an enterprise and are integrated with the management process:
I. Internal environment
II. Objective setting
III. Event identification
IV. Risk assessment
V. Risk response
VI. Control activities
VII. Information and communication
VIII. Monitoring
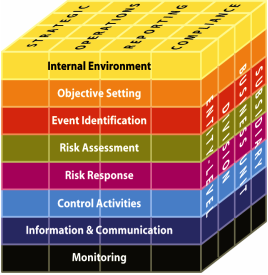
Fig. 1 – COSO’s Enterprise Risk Management – Integrated Framework
4. Once strategy is set, enterprise risk management provides an effective way for management to fulfil its role, knowing that the organization is attuned to risks that can impact strategy and is managing them well.
Applying enterprise risk management helps to create trust and instill confidence in stakeholders in the current environment, which demands greater scrutiny than ever before about how risk is actively addressed and managed. While the management of an enterprise is expected to have a hands-on approach to ERM, the IFSC Authority is expected to provide oversight of enterprise risk management.
5. The objective of this framework is to ensure sustainable growth of the organisation and to promote a proactive approach in identifying, evaluating, reporting, and managing risks associated with its operations. The specific objectives of this framework are:
i) To enable visibility and oversight of the Board on the risk management system and material risk exposures of IFSCA.
ii) To ensure all risks across the organisation are identified and evaluated through a standardized process and consolidated across the organisation to enable risk prioritization.
iii) To ensure mitigation plans for key risks are agreed upon, assigned to risk owners (i.e., Business Units), and reviewed on a periodic basis.
iv) To ensure that risks are reported at all levels in the organisation as per their relevance and significance.
v) To ensure that the risk governance structure is aligned with the organisational structure and risk profile of the organisation with well-defined and delineated roles, responsibilities, and delegation of authority.
vi) To enable transparency of risk management activities with respect to internal and external stakeholders.
vii) To promote confidence in operations, management decisions, and certainty regarding expected outcomes. To enable compliance with appropriate statutory & legal requirements, wherever applicable, through the adoption of leading practices.
viii) To assist in defining the early warning indicators and the related leading measures associated with the top risks identified.
ix) To establish and maintain the risk appetite of the organisation within the defined threshold levels.
x) Assist in safeguarding the value and reputation of the organisation by avoiding unpleasant shocks and surprises.
xi) To develop a “risk aware” culture which is crucial for long-term success.
The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) has been established to regulate and develop financial services in the International Financial Services Centres (IFSCs) located in India.